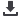
Fig. 6. Values
p
cs
and
p
fs
at
p
r
= 0
,
1
and at different values of
n
and
ε
s
In Fig. 6 the curves intersect at certain values of
n
and
ε
s
. Thus, the
selection of
n
and
ε
s
affects the values
p
cs
and
p
fs
. In case of false detection
of
n
-bit sequence of the synchronization code in the data frame space,
the length of which is
b
bits, the probability of false synchronization is
calculated by the formula
F
= 1
−
(1
−
p
fs
)
b
,
(5)
where
b
=
N
f
−
(
n
)
−
(
n
−
1)
,
(6)
N
f
is the total length of the frame,
n
— is the length of the synchronization
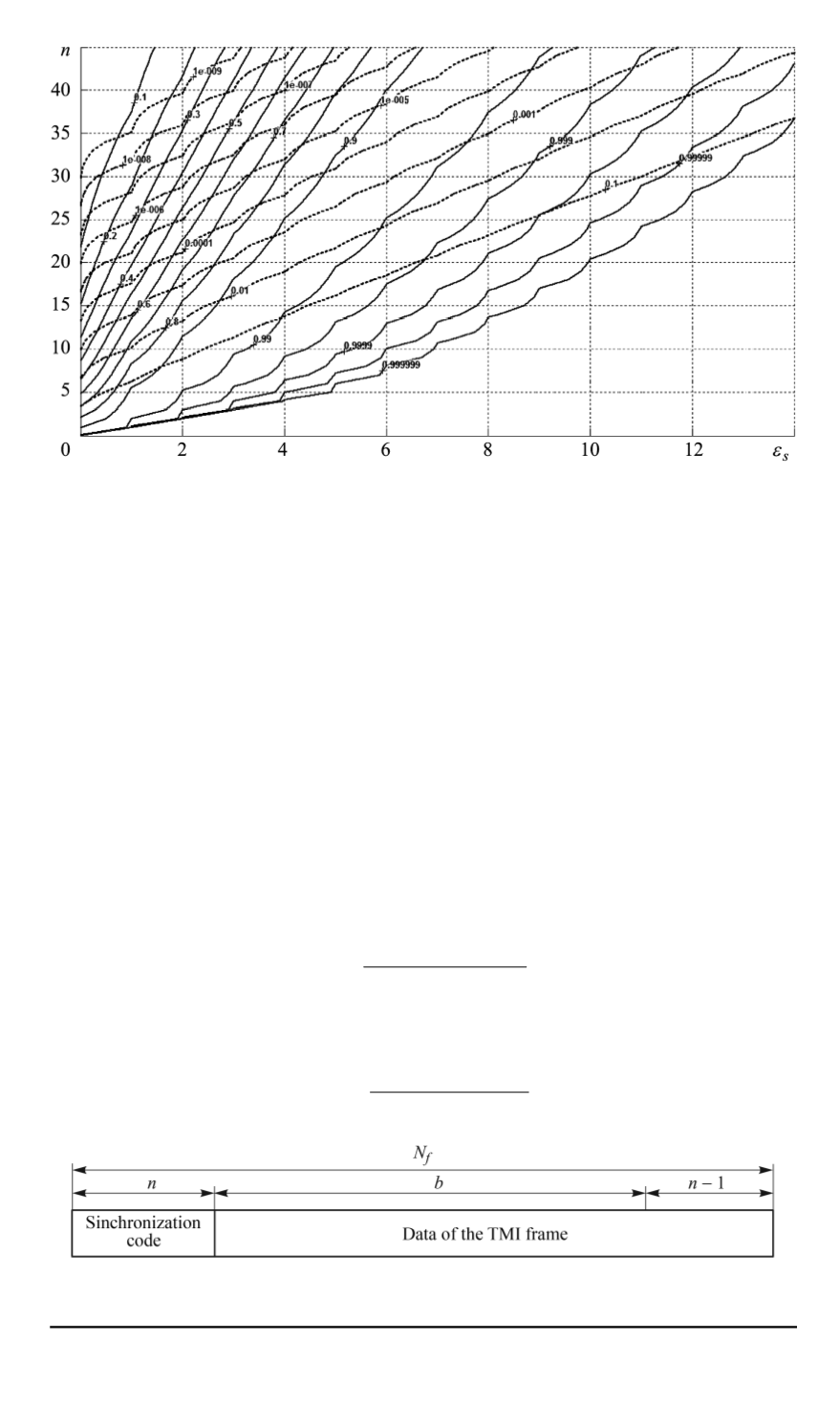
code (Fig. 7).
The probability of making the right decision in the “Search” mode can
be written as:
T
=
p
cs
(1
−
F
)
F
+
p
cs
(1
−
F
)
;
(7)
the probability of making a wrong decision in the “Search” mode has the
following form
W
=
F
F
+
p
cs
(1
−
F
)
,
(8)
Fig. 7. TMI frame structure
ISSN 0236-3933. HERALD of the BMSTU. Series Instrument Engineering. 2015. No. 2 123